ImmuneCellSeq
A Sensitive and Specific Disease Diagnostic
There is an urgent need to develop specific and more sensitive diagnostic assays to:
- Identify infections and predict outcomes from newly emerging pathogens (Mpox, Covid, Zika)
- Evaluate how protective new vaccines are against deadly infections
- Inform doctors on who should recieve treatments for cancers and other diseases
- Diagnose patients for autoimmunity prior to disease onset so preventative measures can be taken
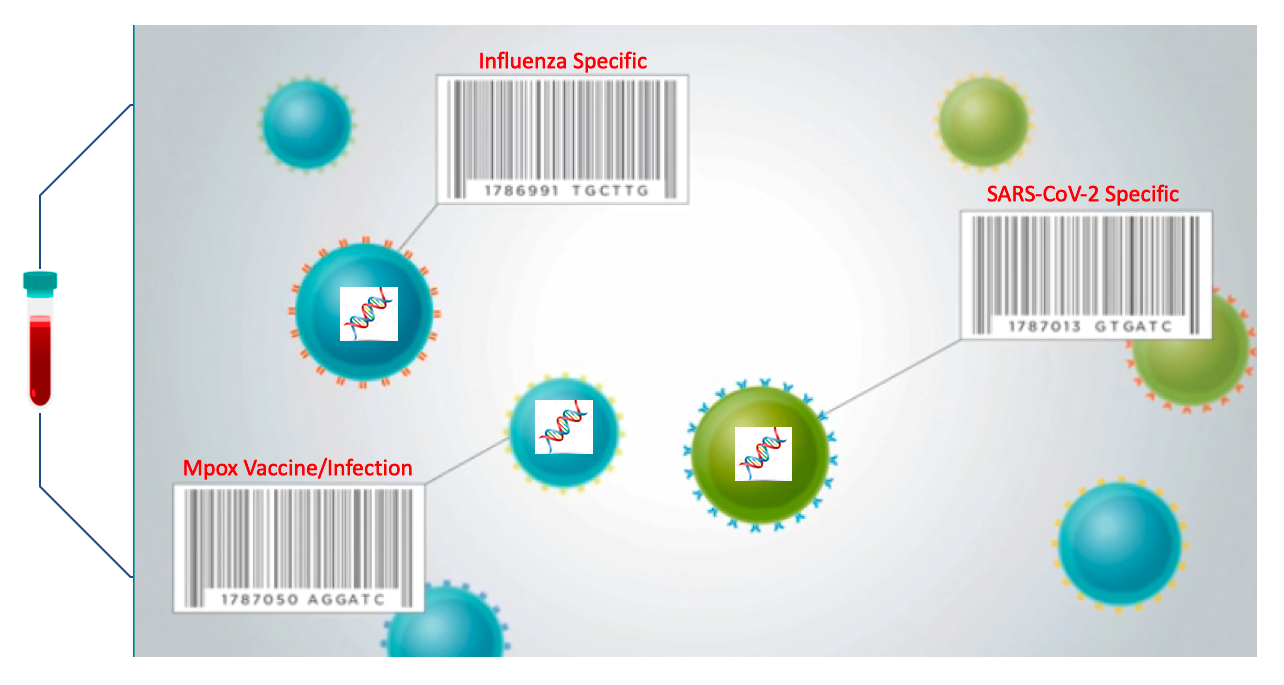
ImmuneCellSeq uses machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to develop diagnostic assays based on genomic data extracted from immune cells (T cells) in a small amount of blood. This web-based machine learning diagnostic platform will enable medical professionals to run diagnostic assays that will assist in properly diagnosing disease and providing medical care. It can be used by scientists to assess new treatments for infectious agents, cancer, and chronic inflamitory diseases.
We can decode Immune Responses to Diagnose Diseases
Sequencing T cell receptors (TCR) can provide us with a robust resource for understanding whether an individual has been infected with a pathogen after the infection occurred. Even after the infection is eliminated, pathogen-specific immune cells and their receptor sequences are present at higher frequencies than prior to infection, and their increase in frequency prevents secondary infections. As a result of this persistence in the body, analyzing the large and diverse TCR repertoires may help improve our understanding of the immune system features and disease progression. We developed a scalable deep neural network model to advance our capabilities of identifying infections from pathogen-specific TCR sequences in circulation over time with exceptional sensitivity.
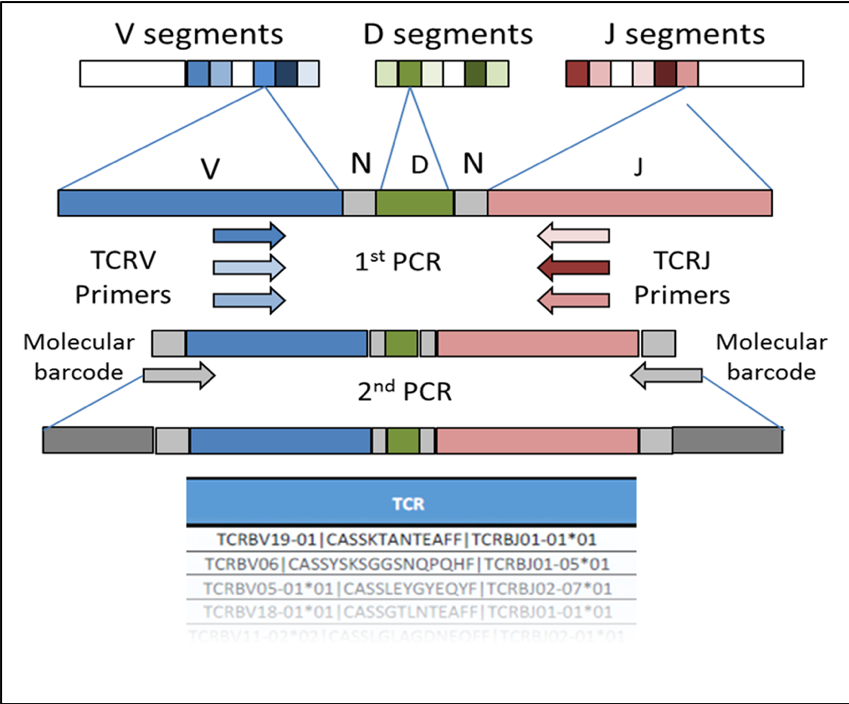
The formation of a TCRβ chain from the random selection and recombination of the V, D, and J segments. While the V and J segments of the TCR locus can be influenced by a patient's major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The CDR3 segment is solely antigen specific.
Capabilities
| Species | Disease Classifier |
|---|---|
| Human | Covid |
| Human | Smallpox Vaccine |
| Mouse | Mpox |
| Mouse | Smallpox Vaccine |
ImmuneCellSeq Demonstrations
Demonstration Table
The table below runs the classifiers using the TCR sequences listed along side it.
Click the run button on any row and the classifier will be run with the data file in the table.
The result from running the classifer will display on the right providing the results from the classifier.
| Species | Classifier | Status | File | |
| Human | Covid | Positive | ||
| Human | Covid | Negative | ||
| Human | Smallpox Vaccine | Positive | ||
| Human | Smallpox Vaccine | Negative | ||
| Mouse | Mpox | Positive | ||
| Mouse | Mpox | Negative | ||
| Mouse | Smallpox Vaccine | Positive | ||
| Mouse | Smallpox Vaccine | Negative |
Test Results
Demonstration Form
The form below allows for the download of a random TCR sample, and the ability to run that sample with the classifier.
To download a sample select the desired species and classifer from the dropdowns. A sample will be randomly selected.
The downloaded file will be named based on the species, classifier, and expected sample output (positive or negative).
To run the classifer, select the desired species and sample from the dropdowns and upload the TCR sample.
The result from the classifier will display below the form.
Model Results
Publications
| A Rajeh, K Wolf, C Schiebout, N Sait, T Kosfeld, RJ DiPaolo* and TH Ahn*, "iCAT: diagnostic assessment tool of immunological history using high-throughput T-cell receptor sequencing", F1000Research, 2021. |
| Mariah Hassert, Kyle J. Wolf, Ahmad Rajeh, Courtney Shiebout, Stella G. Hoft, Tae-Hyuk Ahn, Richard J. DiPaolo, James D. Brien, Amelia K. Pinto, "Diagnostic differentiation of Zika and dengue virus exposure by analyzing T cell receptor sequences from peripheral blood of infected HLA-A2 transgenic mice", PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2020. |
| Tim Kosfeld, Jonathan McMillan, Richard J. DiPaolo, Jie Hou*, and Tae-Hyuk Ahn*, "Performance Evaluation of Viral Infection Diagnosis using T-Cell Receptor Sequence and Artificial Intelligence", in Proceedings of the 11th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics (BCB ’20), September 21--24, 2020, Virtual Event, USA, 2020. |
| K. Wolf, T. Hether, P. Gilchuk, A. Kumar, A. Rajeh, C. Schiebout, J. Maybruck, R. M. Buller, T.-H. Ahn, S. Joyce, R. DiPaolo, "Identifying and Tracking Low Frequency Virus-Specific TCR Clonotypes Using High-Throughput Sequencing", Cell Reports, VOLUME 25, ISSUE 9, P2369-2378.E4, 2018 |